Manage Credentials
You can create credentials, list credentials, or delete credentials in your Autonomous AI Database.
- Create Credentials to Access Cloud Services
To access services in the Cloud, such as Cloud Object Store, you first need to create credentials in your Autonomous AI Database. - Create Credentials to Access Cloud Services in Cloud Shell
Use Cloud Shell to run a script that creates OCI Native Credentials and Auth Token in your Autonomous AI Database. - List Credentials
DBMS_CLOUDprovides the ability to store credentials using the procedureDBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL. You can list credentials from the viewALL_CREDENTIALS. - Delete Credentials
DBMS_CLOUDprovides the ability to store credentials using the procedureDBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL. You can remove credentials withDBMS_CLOUD.DROP_CREDENTIAL.
Create Credentials to Access Cloud Services
To access services in the Cloud, such as Cloud Object Store, you first need to create credentials in your Autonomous AI Database.
Parent topic: Manage Credentials
Create Credentials to Access Cloud Services in Cloud Shell
Use Cloud Shell to run a script that creates OCI Native Credentials and Auth Token in your Autonomous AI Database.
To create credentials using the DBMS_CLOUD package, see Create Credentials to Access Cloud Services and CREATE_CREDENTIAL Procedure.
- About the Create Credential Cloud Shell Script
Run the Create Credential Cloud Shell script in the Cloud Shell developer tool to generate credential scripts to run in your Autonomous AI Database. - Example: Create OCI Native Credentials
This example uses Cloud Shell to run the Create Credential script to create OCI Native Credential scripts. - Example: Create OCI Native Credentials and Run in Autonomous AI Database
This example uses the Create Credential script to create an OCI Native Credential script that is run in your Autonomous AI Database. - Create Auth Token Used for Swift Credential
If you want to create an Auth Token/Swift credential, though Oracle recommends the use of OCI Native Credentials, include the--allargument when running the script to generate OCI Native Credentials and the Auth Token/Swift credential.
Parent topic: Manage Credentials
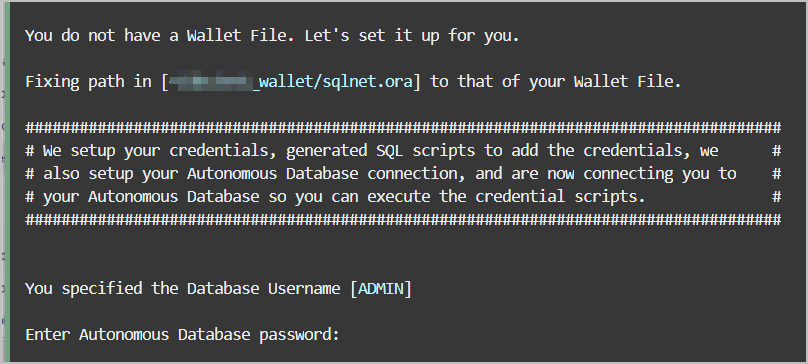
About the Create Credential Cloud Shell Script
Run the Create Credential Cloud Shell script in the Cloud Shell developer tool to generate credential scripts to run in your Autonomous AI Database.
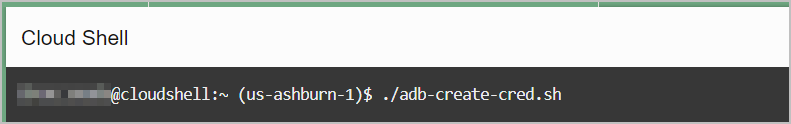
Use the Create Credential script, adb-create-cred.sh, to create new or
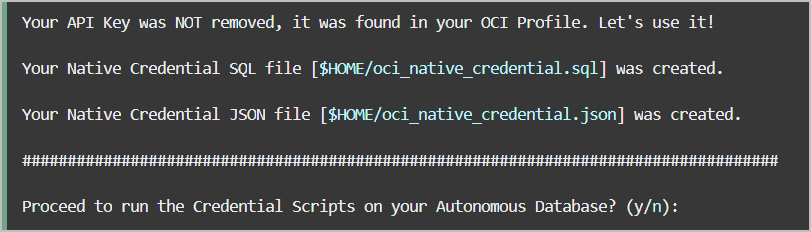
to reuse existing OCI Native Credentials, including an RSA key pair with a fingerprint.
The credentials are provided to the user in the form of scripts,
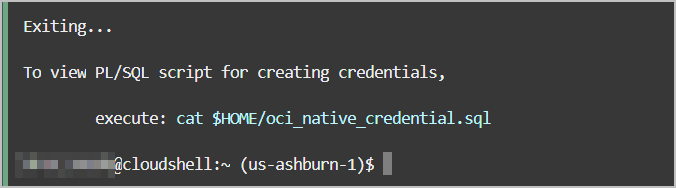
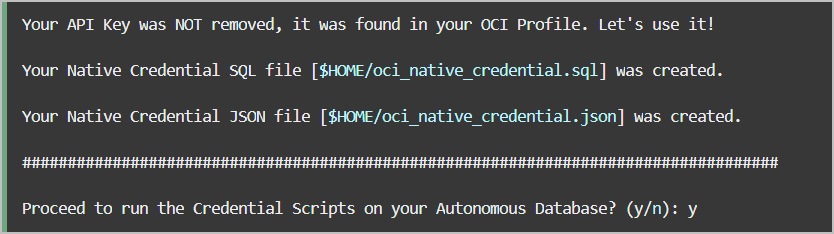
oci_native_credential.sql and
oci_native_credential.json, that can be run in your Autonomous AI Database. Existing credentials are
backed up if new credentials are created.
Use the adb-create-cred.sh script to run the generated credential
scripts in your Autonomous AI Database or exit
the program and run the scripts in your database with a SQL or JSON compatible tool or
utility of your choice. See Example: Create OCI Native Credentials and Example: Create OCI Native Credentials and Run in Autonomous AI Database for more information and examples.
Optionally, adb-create-cred.sh is used to create Auth Token/Swift
credentials. Oracle recommends the use of OCI Native Credentials. However, if you want
to create an Auth Token/Swift credential, it is supported by this shell script. See
Create Auth Token Used for Swift Credential for details.
If for you do not have access to the Cloud Shell developer tool, create OCI Native Credentials without using the
adb-create-cred.sh script. See Create Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Native Credentials for
details.
Example: Create OCI Native Credentials
This example uses Cloud Shell to run the Create Credential script to create OCI Native Credential scripts.
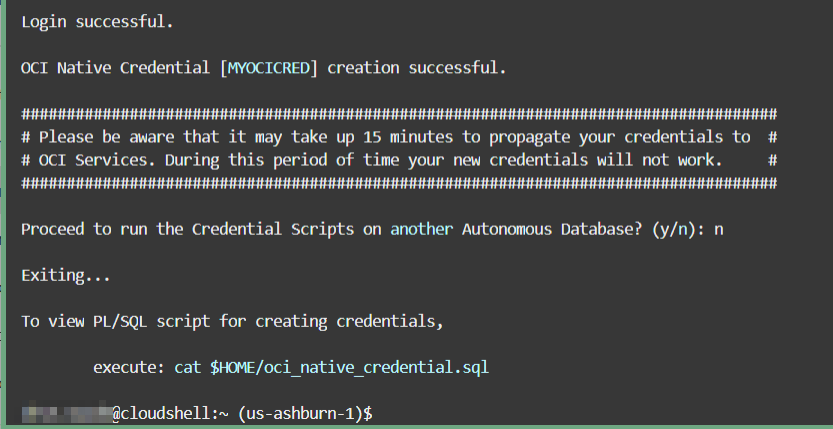
Run adb-create-cred.sh to generate
credential scripts, oci_native_cred.sql and
oci_native_cred.json. The
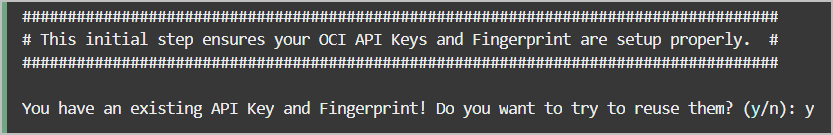
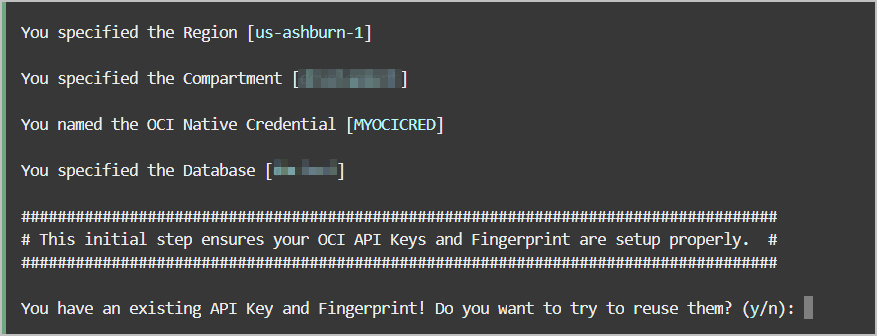
adb-create-cred.sh script searches for
existing credentials, if found you are asked if you want to reuse
them or if you want new credentials created. Depending on your
decision, the generated credential scripts include new or existing
credentials. Download the OCI Native Credential script or copy it to
run it directly in your database using any SQL or JSON tool or
utility.
For a list of arguments supported by the Create Credential script, enter
adb-create-cred.sh --help.
In this example, OCI Native Credential scripts are generated for your tenancy without running them in your database. See Example: Create OCI Native Credentials and Run in Autonomous AI Database, for an example of running the OCI Native Credential script in your database.
Example: Create OCI Native Credentials and Run in Autonomous AI Database
This example uses the Create Credential script to create an OCI Native Credential script that is run in your Autonomous AI Database.
- (Optional) Provide the database region, compartment and database name, to avoid having the script search for the database. Although these options are not required, they can save processing time, especially on tenancies spanning a multitude of compartments and Autonomous Databases.
- The script assumes the database is in your home region. If it is
in a different region, you must pass in the region name argument,
--region, when running the script. - If you don't provide the compartment (--compartment), or database name (--database), the script searches for possible candidates and prompts you to make a selection from lists of possible compartments and databases.
- To list available options, enter
-hor--help.
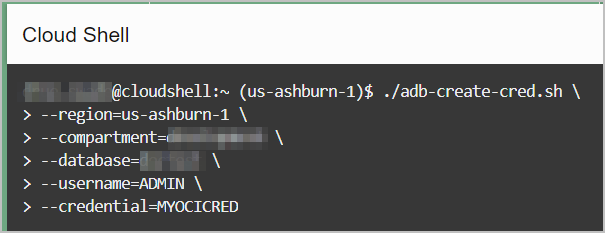
In the following example, the Create OCI Native Credential script,
adb-create-cred.sh, is used to generate a credential script
with existing credentials and run the script in a specified database.
The database region, compartment, and name are passed as arguments to the
script. The --database option requires both
--region and --compartment. If you specify
only --database without these, then the option is ignored.
For a list of arguments supported by the Create Credential script, enter
adb-create-cred.sh
--help.
Create Auth Token Used for Swift Credential
If you want to create an Auth Token/Swift credential, though Oracle
recommends the use of OCI Native Credentials, include the --all argument
when running the script to generate OCI Native Credentials and the Auth Token/Swift
credential.
adb-create-cred.sh --allWhen this flag is used, the script asks if you want to include an Auth Token.
By answering y, your Auth Token key is generated and uploaded to your OCI
profile, and the oci_auth_token_credential.sql and
auth_token.tok scripts are created.
- Run the
oci_auth_token_credential.sqlscript from the Cloud Shell, to create the Auth Token key in your database. The Auth Token key is the value of thepasswordparameter forDBMS_CLOUD_CREATE_CREDENTIAL. - View
auth_token.tokfrom the Cloud Shell. Your Auth Token is the value oftoken.
List Credentials
DBMS_CLOUD provides the ability to store
credentials using the procedure DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL. You can list credentials from the view
ALL_CREDENTIALS.
For example, to list credentials, run the following command:
SELECT credential_name, username, comments FROM all_credentials;
CREDENTIAL_NAME USERNAME
---------------------------–----------------------------- --------------------
COMMENTS
---------------------------–----------------------------- --------------------
ADB_TOKEN user_name@example.com
{"comments":"Created via DBMS_CLOUD.create_credential"}
DEF_CRED_NAME user_name@example.com
{"comments":"Created via DBMS_CLOUD.create_credential"}
See ALL_CREDENTIALS for more information.
Parent topic: Manage Credentials
Delete Credentials
DBMS_CLOUD provides the ability to store
credentials using the procedure DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL. You can remove credentials with DBMS_CLOUD.DROP_CREDENTIAL.
For example, to remove the credential named DEF_CRED_NAME, run the following command:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.DROP_CREDENTIAL('DEF_CRED_NAME');
END;
For more information about the DBMS_CLOUD procedures and parameters, see DBMS_CLOUD Subprograms and REST APIs.
Parent topic: Manage Credentials