ODB Peering Connection
An ODB peering connection allows to set up a peering connection between ODB Network and a VPC which enables applications to connect to your Exadata Database.
A VPC can establish multiple peering connections to different ODB Networks, but only one peering connection to each ODB Network. You can create an ODB peering connection in the same AWS account as the ODB Network, or in a different AWS account after the ODB Network has been shared using AWS RAM.
- Multiple VPCs to one ODB Network – Connect multiple application VPCs to a single ODB Network.
- One VPC to multiple ODB Networks – Connect a single application VPC to multiple ODB Networks.
- An ODB Network supports up to 45 peering connections.
- CIDR blocks must not overlap between the ODB Network and peered VPCs to avoid routing conflicts.
- Supernet CIDR blocks grouping multiple existing subnets are not supported in peered configurations.
- ODB Networks in US East (N. Virginia) and US West (Oregon) created before February 7, 2026, require a network upgrade before adding more than 1 ODB peering. To upgrade, you need to fully recreate your ODB Network. Deleting of ODB Network requires you to delete all Exadata VM Clusters but does not require you to delete or recreate your Exadata Infrastructure.
- Create an ODB Network
- Create a VPC
- Ensure that the ODB network and VPC are not already peered with the each other.
- Creating peering VPC and ODB network in different availability zone(s) (AZ) are supported.
- Modify the ODB peering network CIDR from the trusted account in the ODB peering connection.
- From the Oracle Database@AWS dashboard , select the ODB peering connections button.
- Select the Create ODB peering connection button to start the creation process.
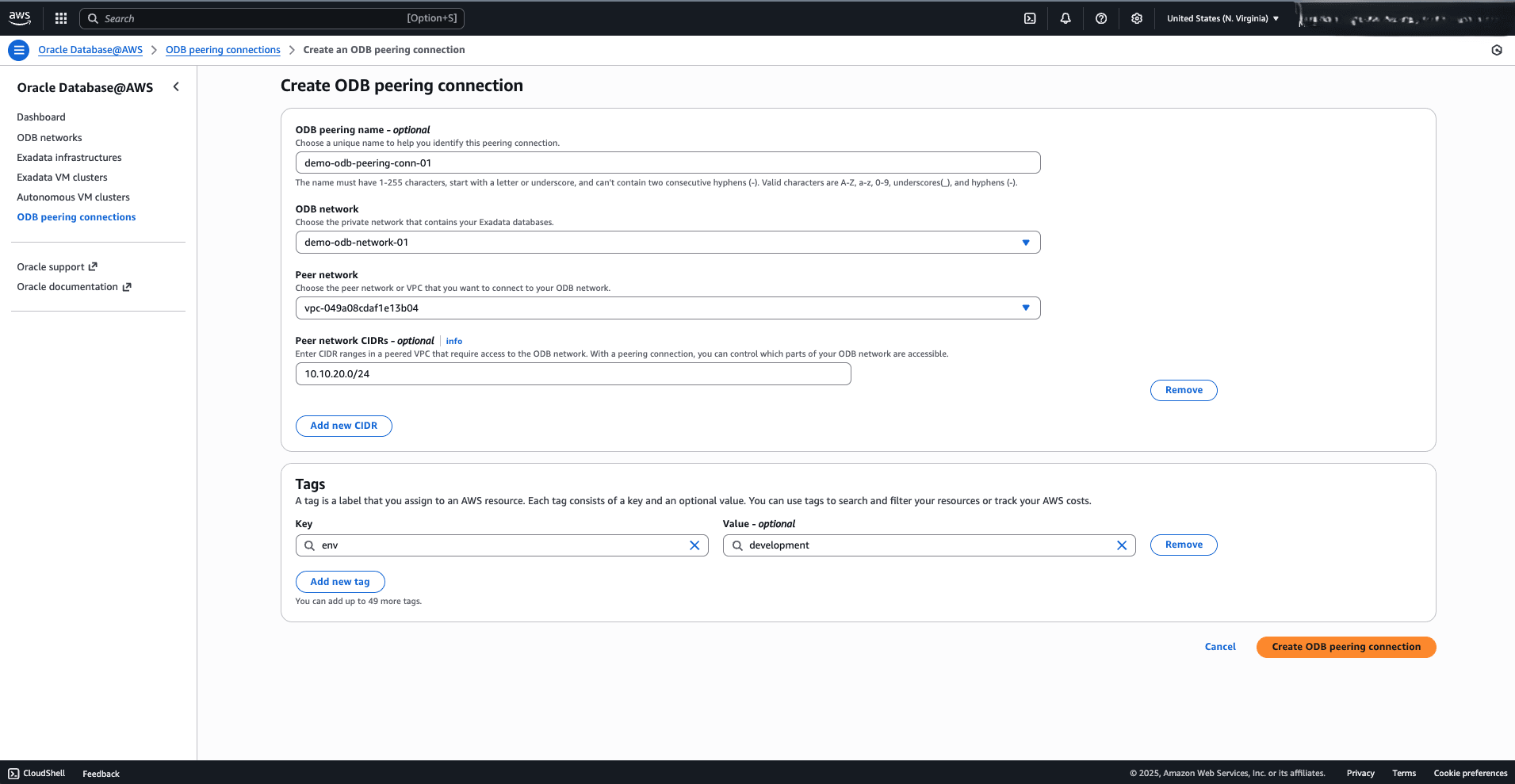
- Enter an unique name in the ODB peering name field.
Note
The ODB peering name can be up to 255 characters. It must start with a letter or underscore (_) and cannot contain two successive hyphens(-). It can include the following characters: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, underscore (_), and dash (-). - From the dropdown list, select the ODB network.
- From your Peer Network dropdown list, select your VPC that you want to pair with your ODB network.
- The Peer networks CIDRs field is optional. Select the Add new CIDR button to add peer network CIDRs.
- If you want to assign a tag to your AWS resources, you can select the Add new tag button, and then enter a key and a value. This step is optional.
- Review the information you entered, and then select the Create ODB peering connection button.
- Once the creation of the ODB peering connection is successful, you will see the success message.
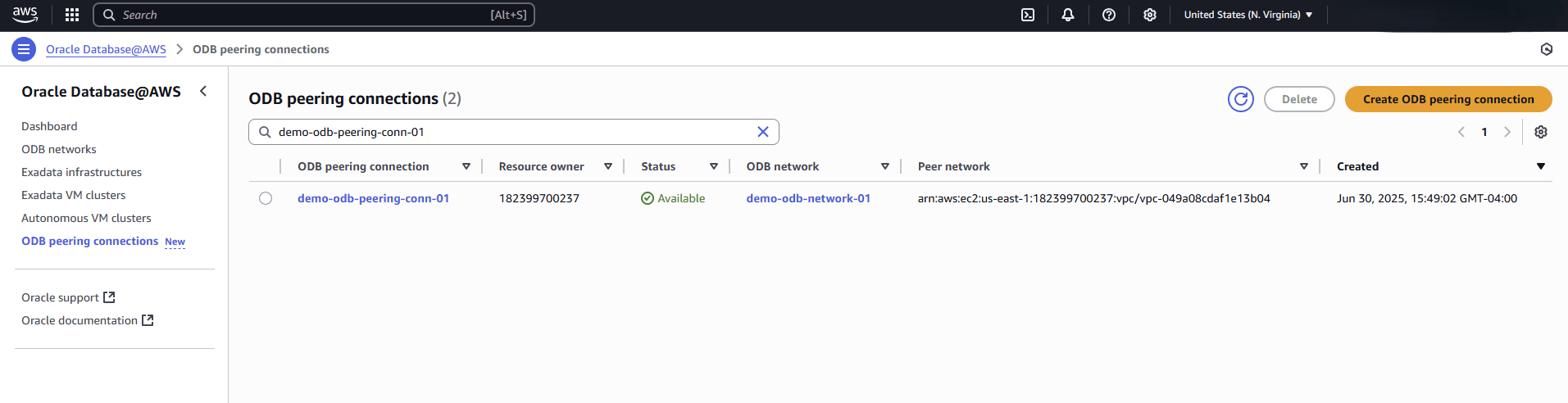
- You can also monitor the status of the provisioning and, once the ODB peering connection is active, review its details from the ODB peering connections list.
- Once the ODB peering connection is created, you can view the details of it from the ODB peering connections list on the Oracle Database@AWS dashboard.
ODB peering connection creation is only available through the AWS Console and AWS CLI.
There is currently no content for this page. Oracle Database@AWS team intends to add content here, and this placeholder text is provided until that text is added. The Oracle Database@AWS team is excited about future new features, enhancements, and fixes to this product and this accompanying documentation. We strongly recommend you watch this page for those updates.
ODB peering connection creation is only available through the AWS Console and AWS CLI.
You can provision an ODB peering connection in AWS using the Terraform Provider hashicorp/aws (version 6.15.0 or higher).
Prerequisites- Terraform or OpenTofu installed
- AWS credentials configured
- HashiCorp AWS provider version >= 6.15.0
- Provision of an ODB Network and a VPC
# Prerequisites: Application VPC with a Workload Subnet for ODB Peering Connection module "app_vpc" { source = "aws-ia/vpc/aws" version = "4.5.0" name = "tf-vpc-demo" azs = ["us-west-2c"] cidr_block = "10.30.0.0/16" subnets = { workload = { cidrs = ["10.30.1.0/24"] } } }
Sample Terraform ConfigurationFor detailed configuration options, see aws_odb_network_peering_connection.locals { # IDs of depending resources peer_network_id = module.app_vpc.vpc_attributes.id odb_network_id = aws_odb_network.this.id } # Create a Peering Connection between the ODB Network and the VPC resource "aws_odb_network_peering_connection" "this" { # Optional explicit dependencies depends_on = [ aws_odb_network.this, module.app_vpc ] # Required Arguments odb_network_id = local.odb_network_id peer_network_id = local.peer_network_id display_name = "tf-odb-peering-conn-demo" # Optional Arguments region = "us-west-2" tags = { created_via = "terraform" env = "demo" } }Reference Implementation
To review examples of integrated Terraform solutions, see the terraform-oci-multicloud-aws GitHub repository.
What's Next?
Create an Exadata Database or Autonomous AI Database.